You’ve finished remediation. The worst barriers are gone, and your team takes a well-earned victory lap. A few weeks later, though, a plugin gets updated, marketing adds a third-party widget, a dev ships a “harmless” CSS tweak—and suddenly a button loses its visible focus style, a modal traps keyboard users, and checkout errors stop announcing to screen readers.
That’s how the web works: a website is a living system. Content, components, dependencies, and integrations are always in motion. And it doesn’t take a major redesign to break something important—sometimes a “quick fix” is all it takes to undo months of good work.
That raises the question: Is it enough to lean on free browser tools for occasional spot checks, or is it time to invest in accessibility monitoring that gives you steady, ongoing confidence?
In this guide, we’ll compare both paths—cost, coverage, reliability, risk, and effort. We’ll also share a hybrid approach that many teams prefer and show how a11y.Radar (216digital’s monitoring solution) helps you protect the remediation you’ve already paid for while keeping team workload predictable.
Why Ongoing Accessibility Monitoring Matters (Even After You “Pass”)
Think of accessibility like security, uptime, or SEO: you don’t check once and call it done—you maintain it. After remediation, your site is in a good place. But change is constant, and those changes often show up in small, easy-to-miss ways, such as:
- A new banner, analytics script, or carousel has been added to a key template.
- A cookie-consent update that quietly alters focus management or timing.
- A styling tweak that shifts color contrast or live-region behavior.
Many issues don’t show up on the surface. They appear when people actually interact with your interface—opening a menu, submitting a form, tabbing through a dialog, or switching filters. The more ways people can move through your site, the more opportunities there are for something to break without anyone noticing right away.
Why You Can’t Rely on Users (Or Automation) Alone
As your site grows, so does the number of templates, content authors, and embeds. Every new piece is another opportunity for a regression. Relying on users to report problems means you’ll hear about them late, and often in a very public way. At the same time, you already know that meaningful issues in mature audits usually need human judgment; automation alone can’t replicate a real person moving through real flows.
Monitoring isn’t about chasing scores. It’s a way to catch small cracks early, before they turn into costly gaps that affect both user experience and your team’s time.
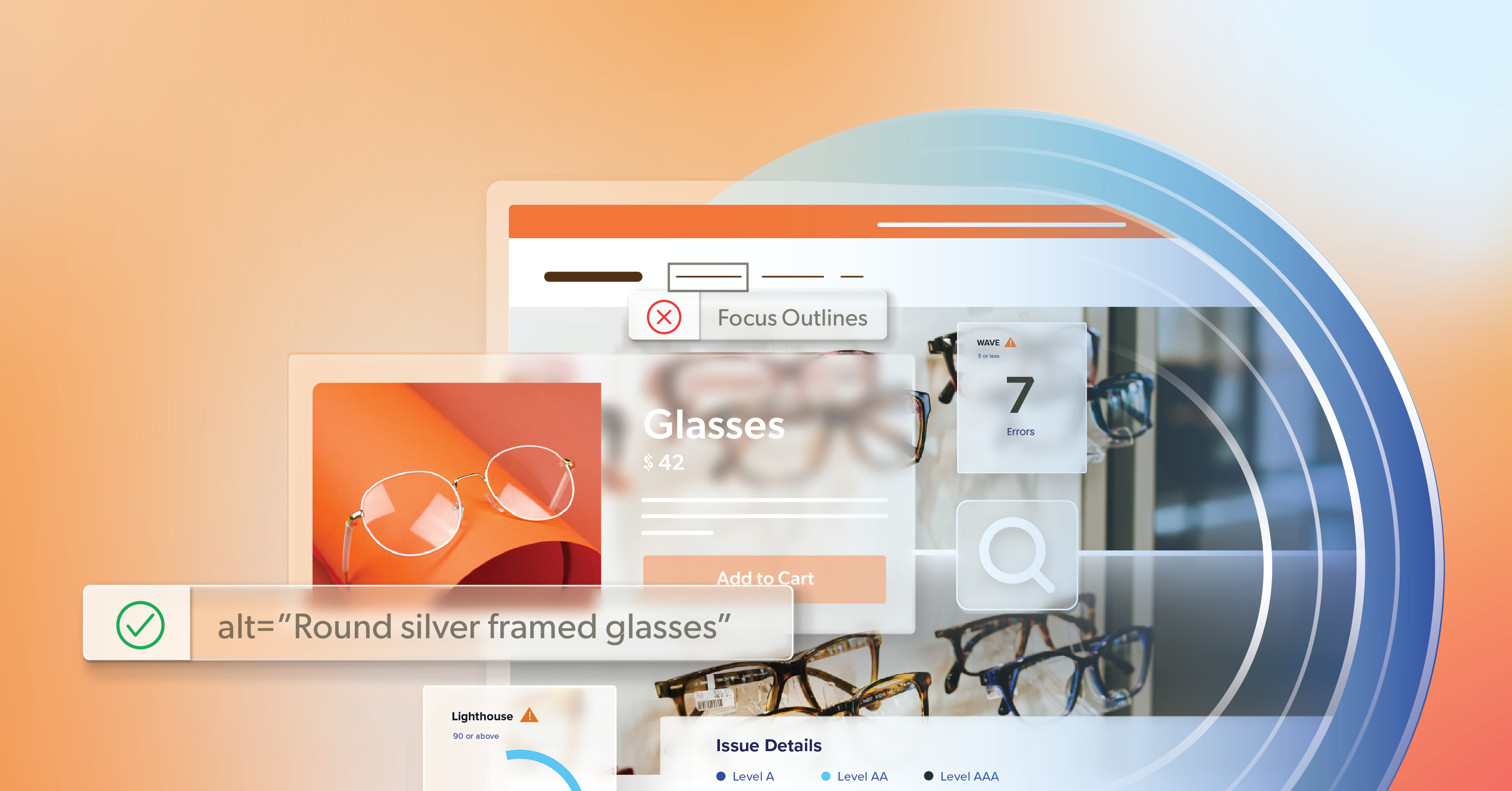
Free Browser Tools: What Are They and Where They Fall Short
You already know the classics, like Google Lighthouse in Chrome DevTools. They’re fast, free, and helpful, and they absolutely deserve a place in your process.
These tools shine in moments like:
- Running checks during development or PR review to catch obvious misses such as missing alt text, ARIA misuse, or color-contrast problems.
- Iterating on a single component or template where quick, page-level feedback keeps improvements moving.
In those contexts, it’s easy to run Lighthouse on a single page, surface immediate issues, and point engineers straight to the right fixes.
Where Free Web Accessibility Tools Fall Short
The challenge comes when you try to stretch these tools beyond what they were designed to do. Page-by-page checks don’t give you site-wide visibility, automated drift detection, or a sense of how issues are spreading across templates. Most free scans don’t simulate realistic user journeys—checkout, sign-up, multi-step forms—so serious interaction problems can stay hidden. You also don’t get alerts, historical trends, or reports to show what’s getting better or worse over time.
On top of that, the signal can be noisy. Some findings are low impact or turn out to be false positives, while other high-impact problems never surface at all without human testing. Free tools are fantastic tactical helpers, but they aren’t a complete plan for accessibility monitoring at scale.
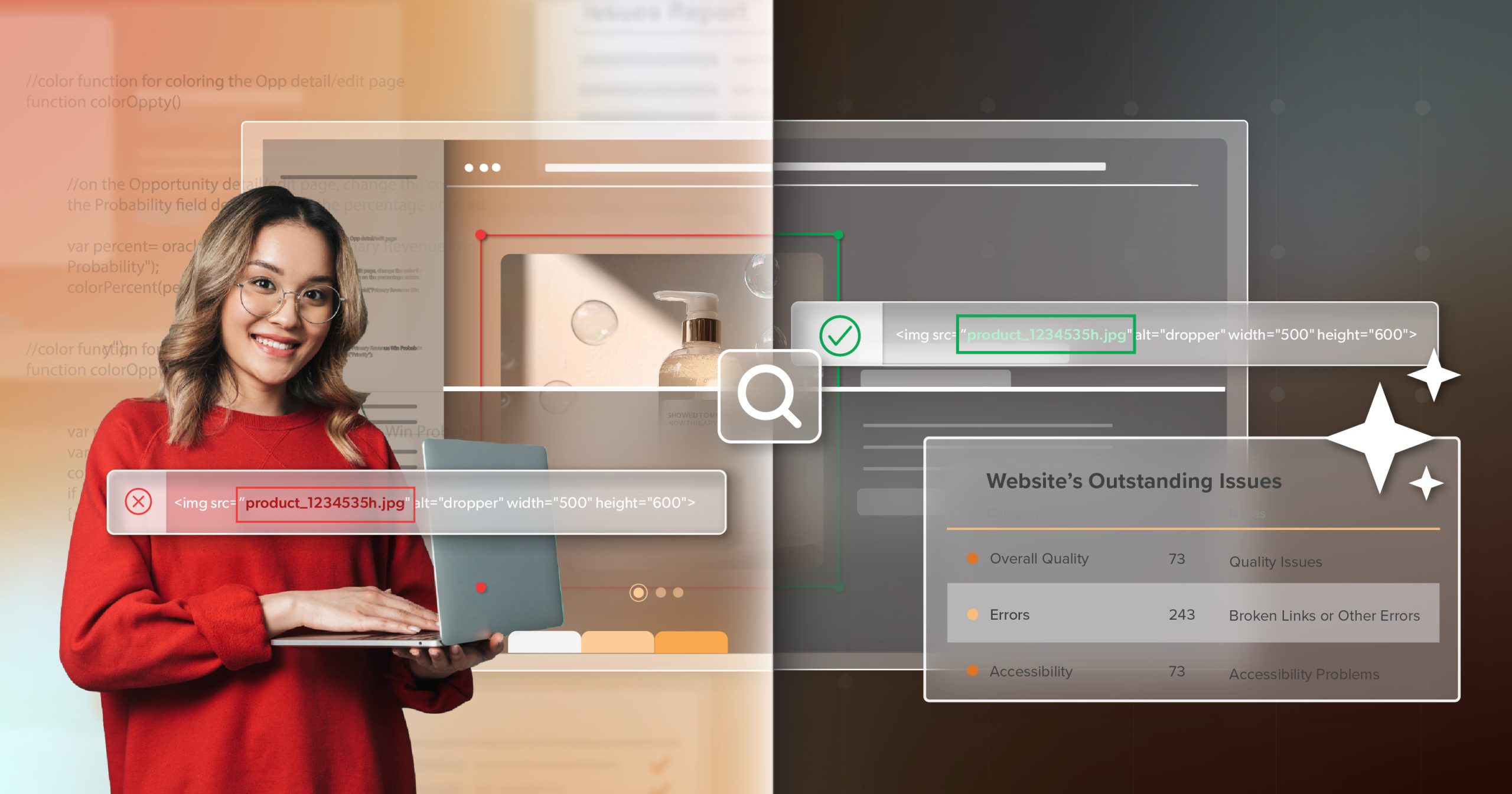
The Hidden Costs of “Free”
“Free” starts to look expensive once you factor in the time your team spends and the risk your organization carries.
Manually scanning individual pages doesn’t scale well as your catalog, blog, or application grows. Over time, consistency slips, and gaps appear between what you intend to check and what actually gets checked. Without any alerting, a broken label or focus trap can sit unnoticed for weeks, frustrating users and quietly hurting conversions.
Risk and False Confidence
A green Lighthouse score can also create a false sense of security. It doesn’t cover complex interactions or conditional content, and it can’t guarantee that every critical flow is usable with assistive technology or only a keyboard. Meanwhile, if a barrier exists when a user needs to complete a task, “we thought we were compliant” won’t help much in a legal or reputational crisis.
The Retrofit Tax
There’s also the retrofit tax to consider. The longer a bug lives, the more it costs to fix—especially when it becomes part of a shared design system or depends on a third-party script. A helpful gut-check is this: if a critical flow broke tonight, how would you know—and how quickly could you respond?
What Paid Accessibility Monitoring Adds That Free Tools Can’t
A professional monitoring platform isn’t just “more scans.” It’s a system designed to help keep your site accessible over time, even as everything around it changes.
Instead of manually spot-checking individual URLs, automated site-wide crawls scan your core templates and priority pages on a schedule. When a regression appears—maybe a template shifts, a new blocker arrives, or a dependency change breaks a pattern—the platform can surface that change quickly with contextual checks and alerts, so the right people hear about it while the issue is still small.
Turning Findings Into Action
Dashboards and trend lines turn those scans into something you can act on: you see what’s improving, what’s slipping, and where to focus next, with numbers you can share in reports. Integrations with tools like Jira or GitHub let you turn findings into tickets, assign owners, and track SLAs just like any other quality work. At the same time, an audit trail and documentation give you a record of what was found, when, and how it was resolved—valuable for compliance, procurement, and legal conversations.
Scaling Without Burning Out Your Team
Most importantly, a paid accessibility monitoring approach scales with you. As content and complexity grow, the system keeps up without burning out your developers, turning panicked fire drills into a more predictable subscription and a steadier workflow.
A Practical Way to Decide: Budget, Scale, Confidence
You don’t have to choose between “only free” or “only paid.” Many teams blend both, matching their approach to their personal constraints.
If your site is small, built on a limited set of templates, and doesn’t change very often, you may find that free tools plus periodic professional audits are enough—especially if your legal exposure is relatively low and you can plan for a full review once or twice a year.
On the other hand, if you’re working with a medium or large site or application, have frequent releases and many contributors, or maintain complex flows like checkout, applications, or authenticated account areas, the calculus changes. Higher-risk environments—enterprise, healthcare, finance, public sector—often need more confidence, along with leadership-level reporting and accountability, and that’s where continuous accessibility monitoring becomes hard to ignore.
Why a Hybrid Strategy Often Wins
A hybrid strategy often gives the best of both worlds. Free tools stay in the development workflow to support dev speed: run Lighthouse and similar tools during builds and code reviews to catch obvious misses early. Accessibility monitoring then sits underneath as a safety net, catching drift, regressions, and wide-impact issues across the site. Because everyone—from product managers to executives—can see how things are trending, accessibility becomes a shared responsibility, not a side project.
Think of it like uptime: you still write resilient code, but you also run monitoring so you know when something fails.
a11y.Radar: Ongoing Accessibility Monitoring, Minus the Guesswork
After helping hundreds of organizations remediate, we built Accessibility Radar (a11y.Radar) at 216digital to address the problems that show up after the fixes are shipped and celebrated.
a11y.Radar runs recurring crawls aligned to WCAG 2.2 (and ready for future updates), so your coverage keeps pace with current standards instead of freezing at the moment your audit was completed. When something that used to pass starts to fail, regression alerts let your team know quickly, often before users ever notice an issue. An issue dashboard surfaces severity and trends, so you can prioritize the highest-impact work first instead of chasing every minor flag with the same urgency.
How a11y.Radar Works Day to Day
You can also focus directly on key user journeys—checkout, forms, account areas, and other revenue or mission-critical flows—so the scenarios that matter most to your business are watched closely. Workflow integrations mean that findings don’t live in yet another silo; they move into the tools your dev and QA teams already use, via tickets, email, or exports. Context-aware guidance then points teams toward actionable fixes instead of leaving them to interpret raw scanner output alone.
Human Expertise and Real-World Impact
Behind the data is practitioner expertise. You benefit from specialists who spend their days fixing accessibility barriers, not just reading reports. a11y.Radar is human-first by design: it supports the judgment calls automation can’t make and keeps people focused where they add the most value. The result is simple but powerful—you’ve already paid to remediate; now Radar helps you keep that investment working in the background, day after day.
For example, an e-commerce team wrapped up remediation in Q1. By Q2, a marketing embed introduced an off-screen focus trap on mobile filters. Lighthouse runs on individual pages, which looked fine because no one opened the filter drawer during checks. a11y.Radar flagged the regression within 24 hours as part of a scheduled crawl. The team patched the component that same week, preventing a dip in conversions and a wave of support tickets. Because monitoring caught it early, the fix took hours—not weeks.
How to Choose Your Monitoring Setup (and Whether You Need One)
Use this list to map your situation and make a confident choice:
- Site size & complexity
- How many unique templates and components?
- Do you lean heavily on third-party scripts or embeds?
- Are there complex flows such as checkout, onboarding, applications, or donations?
- Update frequency
- How often do you deploy?
- How many non-dev authors can publish or update content (marketing, merchandising, HR, communications)?
- Team capacity
- Do you have in-house accessibility expertise?
- Can dev and QA dedicate consistent time to triage and fixes?
- Risk tolerance
- What is the cost if a key task is inaccessible for a week?
- Are you in a regulated or contract-sensitive space?
- Budget philosophy
- Do you prefer a predictable subscription, or are you comfortable with unpredictable “hot-fix” costs and potential legal exposure?
- Evidence & accountability
- Do stakeholders want monthly trends, audit trails, and measurable progress?
How to Interpret Your Answers
If most of your responses fall into the low-complexity, low-velocity, and low-risk range, you’ll probably do well with free tools supported by periodic audits. In that scenario, it may still be worth lightly monitoring your most important templates, but you probably do not need full-scale automation.
When you start to see a mix of medium and high scores—especially around risk, complexity, or how fast you release—continuous monitoring becomes far more valuable. It can help you catch issues earlier, reduce last-minute fire drills, and lower the chances of an expensive surprise.
If your answers land somewhere in the middle, a blended approach often works best: use free tools during development, then layer on a11y.Radar to watch the full site in the background and alert you when something slips.
FAQs: Common Questions About Accessibility Monitoring
If Lighthouse gives me a high score, am I good?
It’s a positive signal, but not a guarantee. Scores don’t validate complex interactions, dynamic states, or multi-step flows.
Can’t we just train employees better?
Training helps a lot, and you should invest in it—but embeds, plugin updates, and code changes still happen. Monitoring catches the issues that training can’t fully prevent.
WHow fast will monitoring pay for itself?
YOften, the first caught regression—such as a broken checkout label, a focus issue in a form, or a contrast change in a primary call-to-action—saves enough support time, lost conversions, or rework to cover months of the subscription.
Do we still need manual testing?
Yes. Complex interactions and edge cases still need human eyes. Monitoring reduces the overall manual volume and helps focus human effort where it matters most.
Remediation Makes You Compliant—Accessibility Monitoring Keeps You There
You’ve already done the hard part: remediation. Now it’s about protecting that work.
Free tools like Lighthouse belong in every developer’s toolbox and should be used often. But on a website that changes weekly—or daily—free spot checks alone won’t provide the continuous, site-wide assurance your users and your stakeholders truly need.
A thoughtful strategy anchored by a11y.Radar gives you that kind of assurance: automated crawls, actionable alerts, trends over time, and an audit trail that holds up under scrutiny. It lowers stress, preserves developer bandwidth, and—most importantly—keeps your experience welcoming and usable for everyone.
If you’d like help choosing the right mix for your site and want to see how a11y.Radar fits into your reality, let’s schedule an ADA briefing with 216digital. We’ll map your risks, walk through a practical setup, and build a plan that keeps accessibility strong and sustainable over the long term.