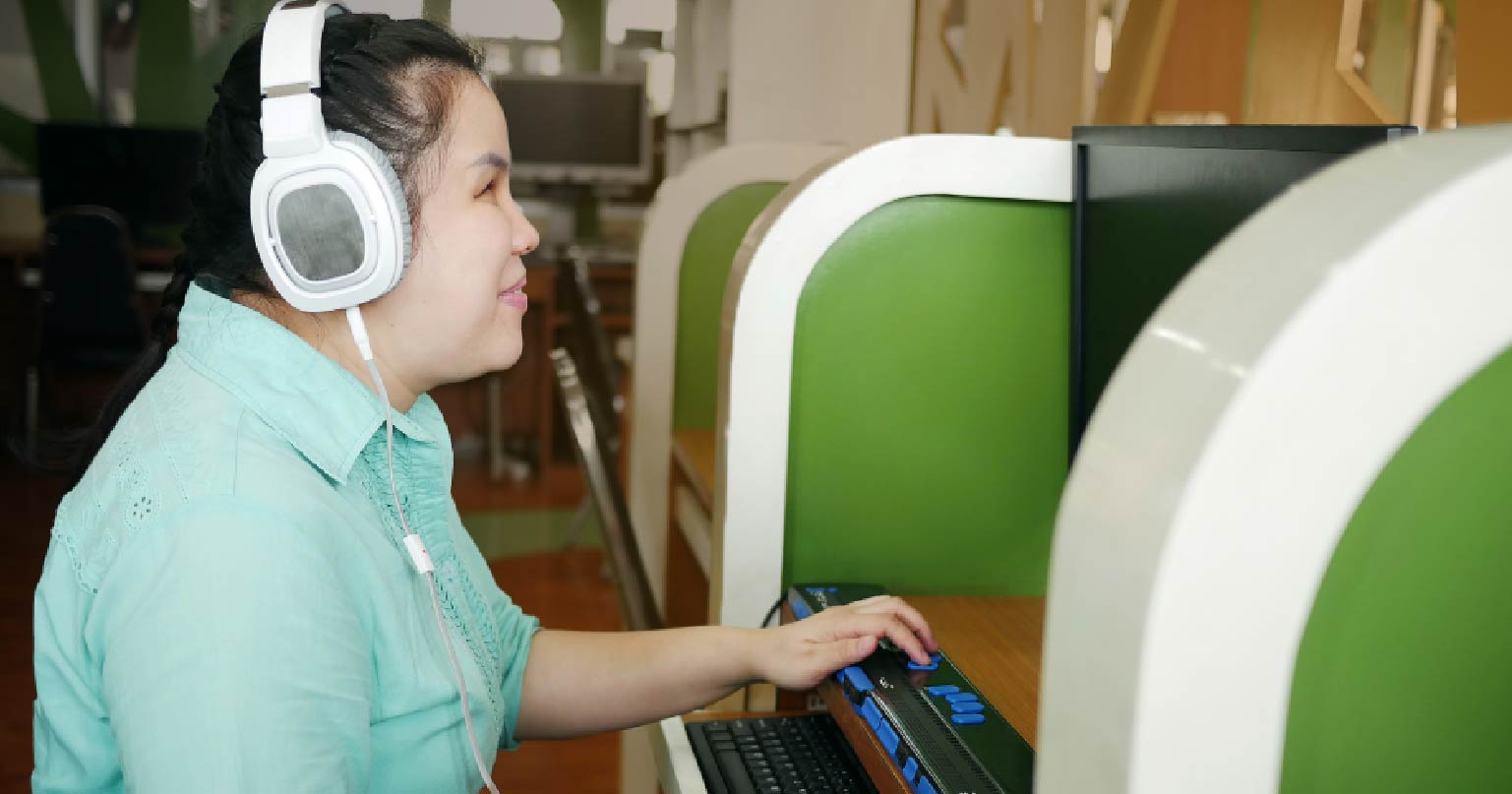
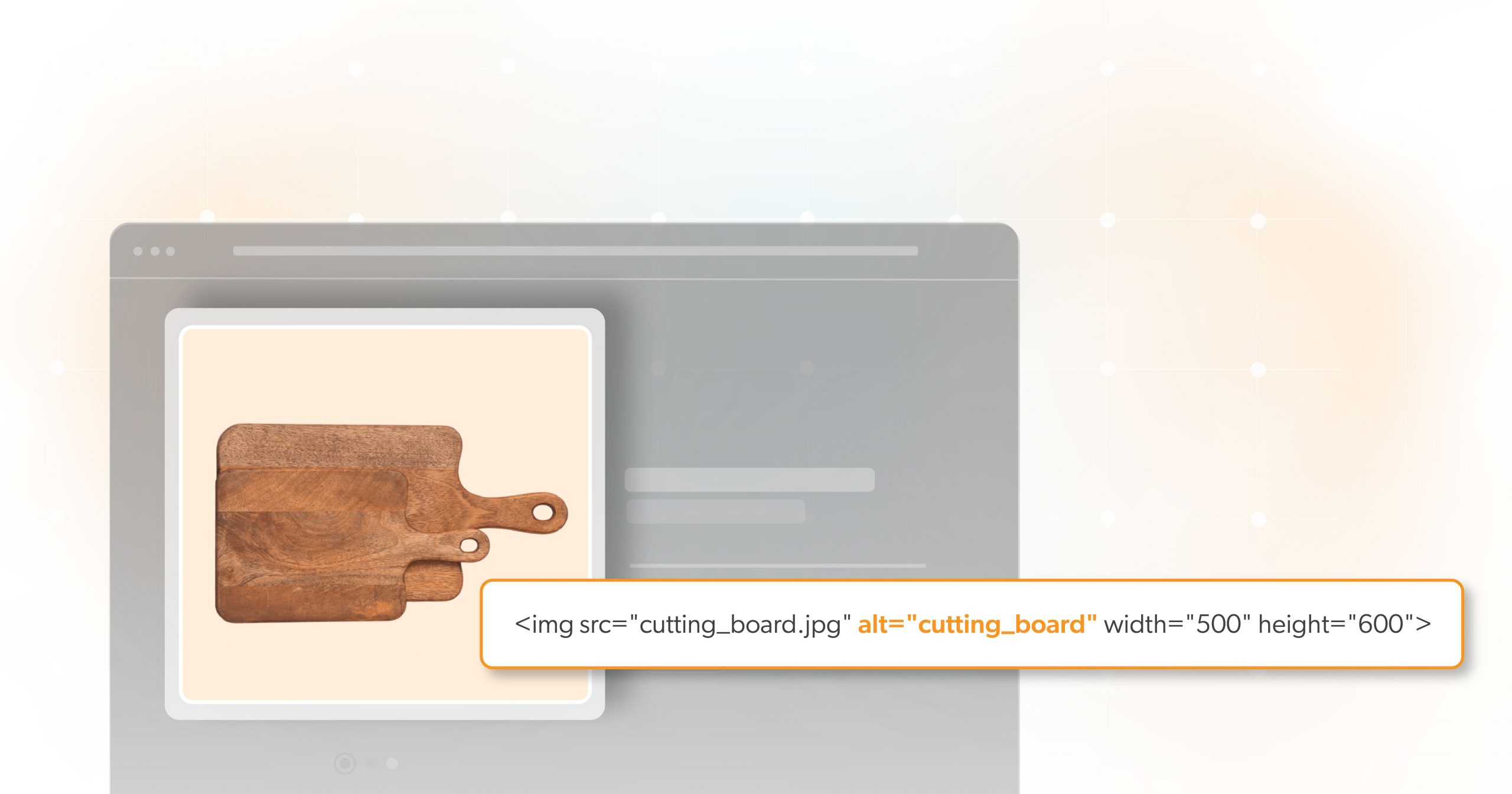
As more businesses move online, understanding web accessibility and ADA compliance becomes crucial. These terms are often used interchangeably but represent different aspects of making a website user-friendly for everyone, including individuals with disabilities. Knowing the distinction between web accessibility and ADA compliance can help protect your business from lawsuits while ensuring your site provides an inclusive experience.
In this article, we’ll examine the definitions of web accessibility and ADA compliance, explore their differences, discuss the legal risks associated with non-compliance, and explain how businesses can proactively address accessibility issues using services like 216digital’s Phase 1 remediation.
What is Web Accessibility?
Web accessibility involves designing and developing websites, tools, and technologies to ensure they are usable by people with a wide range of abilities and disabilities. This includes individuals who have visual, auditory, physical, speech, cognitive, or neurological disabilities. The goal of web accessibility is to ensure that everyone, regardless of their disability, can perceive, understand, navigate, and interact with the web.
Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG)
The primary standard for web accessibility is the Web Content Accessibility Guidelines (WCAG), created by the World Wide Web Consortium (W3C). The latest version, WCAG 2.1, provides a comprehensive set of guidelines aimed at making web content accessible. These guidelines are organized around four core principles, commonly known as POUR:
- Perceivable: Information and user interface components must be presented in ways that all users can perceive.
- Operable: User interface components and navigation must be operable for everyone, including those using assistive technologies like screen readers.
- Understandable: Information and the operation of the user interface must be understandable.
- Robust: Content must be strong enough to work with a wide range of technologies, including those used by people with disabilities.
While WCAG provides the framework for web accessibility, compliance with it is generally voluntary unless law or legal action requires otherwise.
What is ADA Compliance?
ADA compliance refers to meeting the requirements set forth by the Americans with Disabilities Act (ADA), which was enacted in 1990. The ADA mandates that businesses, public services, and other organizations provide equal access to individuals with disabilities. Although the ADA was passed before the internet became mainstream, courts have increasingly ruled that websites are considered public accommodation places, meaning they must be accessible to people with disabilities.
ADA compliance, specifically in the context of websites, refers to whether your site meets the legal requirements of the ADA as interpreted by courts and the Department of Justice (DOJ). No official legal mandate states that WCAG 2.1 must be followed to achieve ADA compliance, but it is widely accepted that adhering to WCAG is the best way to meet ADA requirements.
How Does It Differ From Web Accessibility?
- Web accessibility is the broader concept of ensuring that people of all abilities can use websites.
- ADA compliance is a legal requirement for businesses in the U.S. to provide equal access to individuals with disabilities, which includes making websites accessible.
Web accessibility is a best practice, while ADA compliance is a legal standard. Following web accessibility guidelines, like WCAG 2.1, helps businesses meet the requirements of ADA compliance, but the two terms are not identical.
Is It Possible to Achieve and Maintain Full WCAG 2.1 Compliance?
Yes, but it’s not always easy, especially for bigger, more complex websites. WCAG 2.1 covers a lot of areas—like how text shows up, how media is handled, how forms work, and more. As technology and user needs evolve, keeping up with compliance is an ongoing effort. Regular testing, monitoring, and updates are needed to ensure the site meets the latest accessibility standards.
If you’re worried about protecting yourself from ADA lawsuits, aiming for full WCAG 2.1 compliance is a smart move. It can help reduce your legal risks, but it is only legally required in some cases. Courts have ruled in favor of plaintiffs in ADA lawsuits when websites were not accessible, even if they didn’t meet every single WCAG criterion.
Does Your Website Need to Be Fully Web Accessible to Protect Your Business?
To protect your business from ADA compliance lawsuits, it’s crucial to address the most common accessibility barriers, even if full WCAG 2.1 compliance is not achieved. Many companies focus on making the most essential parts of their website accessible, such as navigation, forms, and checkout processes. This approach can reduce the risk of a lawsuit while allowing businesses to improve their site’s accessibility gradually.
It’s also worth noting that courts have yet to require businesses to meet every WCAG 2.1 guideline to comply with the ADA. However, companies that demonstrate they are actively working to make their sites more accessible—by following best practices and improving critical accessibility issues—are generally better positioned to defend against lawsuits.
The Risk of ADA Compliance Lawsuits
ADA compliance lawsuits have skyrocketed in recent years, especially against businesses with inaccessible websites. These lawsuits can be costly, both in terms of financial settlements and reputational damage. Predatory law firms have begun targeting businesses—tiny and mid-sized companies—that have websites with accessibility issues. These firms often file “copycat” lawsuits, sometimes targeting hundreds of companies with nearly identical complaints.
The financial risk is real. Businesses are often forced to settle the lawsuit or pay legal fees, which can run into tens or even hundreds of thousands of dollars. In addition, businesses may also have to invest in website remediation services to fix accessibility issues.
How Predatory Law Firms Target Websites
Predatory law firms often conduct automated scans of websites to identify accessibility violations, such as missing alt text, poor contrast ratios, or non-functional navigation for keyboard-only users. Once they identify these issues, they send demand letters or file lawsuits, typically hoping that the business will settle quickly to avoid costly litigation.
Unfortunately, even well-meaning businesses that are working on improving accessibility can be targeted. This is why it’s essential to address website accessibility proactively rather than waiting for a lawsuit to happen.
Is Full WCAG 2.1 Compliance Required to Mitigate Lawsuits?
While full WCAG 2.1 compliance is not explicitly required to avoid lawsuits, businesses should aim to make their websites as accessible as possible. The more barriers that are removed, the less likely it is that a website will be the target of a lawsuit.
In most cases, addressing key accessibility issues—such as ensuring all images have alt text, providing video captions, and making the site navigable by keyboard—will significantly reduce the risk of a lawsuit.
Protect Your Business with 216digital
To help businesses avoid the pitfalls of non-compliance, 216digital offers Phase 1 remediation services designed to address the most critical accessibility issues quickly. These services focus on mitigating the risk of ADA lawsuits by resolving common accessibility barriers that predatory law firms often target. By implementing these initial fixes, businesses can start protecting themselves while working toward broader web accessibility goals.
In addition to Phase 1 remediation, 216digital offers ongoing monitoring and testing services to ensure your site remains accessible over time. With a proactive approach, businesses can avoid costly lawsuits and provide a better user experience for all visitors.
Ready to Make Your Website ADA Compliant?
As the digital landscape continues to evolve, ensuring your website is both accessible and ADA-compliant is more important than ever. While full WCAG 2.1 compliance may not always be required, addressing key accessibility issues can significantly reduce your risk of lawsuits and enhance the user experience for all visitors.
Take the next step toward protecting your business and making your website more inclusive. Schedule a personalized ADA compliance briefing with 216digital today. Our team can guide you through Phase 1 remediation and ongoing strategies to keep your site accessible and compliant.