Modern interfaces can be beautiful, fast, and feature-rich, but one truth remains: the browser is ultimately in charge. Your HTML, CSS, and JavaScript make requests—not guarantees. What users experience depends on what the browser chooses to expose. For people using assistive technologies, that experience only works when the interface communicates clearly.
That’s where WCAG 4.1.2 comes in.
This requirement focuses on four foundational properties—Name, State, Role, and Value (NSRV). These properties help browsers and assistive technologies understand what something is and how it behaves. When NSRV is clear and consistent, a button feels like a button, a menu updates when it opens, and a form field tells you exactly what it expects.
For designers and developers who care about creating seamless experiences, WCAG 4.1.2 remains essential. Even in component-driven, JavaScript-heavy environments, NSRV is the common language that keeps everything understandable and usable.
How Browsers, the DOM, and Assistive Tech Communicate
When you write markup, you’re not building the interface directly. You’re describing it. The browser takes those instructions and constructs the Document Object Model (DOM)—a living structure that represents the page.
Different rendering engines—Blink, Gecko, WebKit—may interpret aspects of your code slightly differently. That means accessibility issues can show up even when something “seems fine.”
Here’s the real pipeline:
- Authoring code
- DOM
- Accessibility Tree (AX API mapping)
- Assistive technologies
Each step depends on accurate Name, State, Role, and Value. This idea—programmatic determinability—ensures meaning is exposed in a consistent, machine-readable way. Without that, assistive tech tools can’t reliably describe what’s on the page or what’s changing.
Dynamic pages make this even more important. When menus open, sliders move, or modals appear, assistive tools need updates in real time. If properties don’t update programmatically, users can’t follow what’s happening.
Takeaway: When NSRV is accurate and kept in sync, assistive technologies can deliver the right information at the right time—and every user can understand the interface.
The Core Four: What Each Attribute Means and Why It Matters
Name – What Do We Call It?
The Name is how an element identifies itself to users. This is what screen readers announce.
Examples:
- Button label text
- A
<label>oraria-labelon a form field
Why it matters:Without a Name, users cannot understand what an element does.
Tip: Use visible labels first. ARIA naming is helpful, but visible text supports more users.
Role – What Is It?
The Role tells assistive technologies what kind of element something is—a button, checkbox, link, menu item, slider, and so on.
Example:
<button>has a built-in role- A
<div>acting like a button needsrole="button"(but native is better)
Why it matters: Role sets expectations. Assistive tech knows what kinds of interactions are possible.
Tip: Start with semantic HTML before adding ARIA roles.
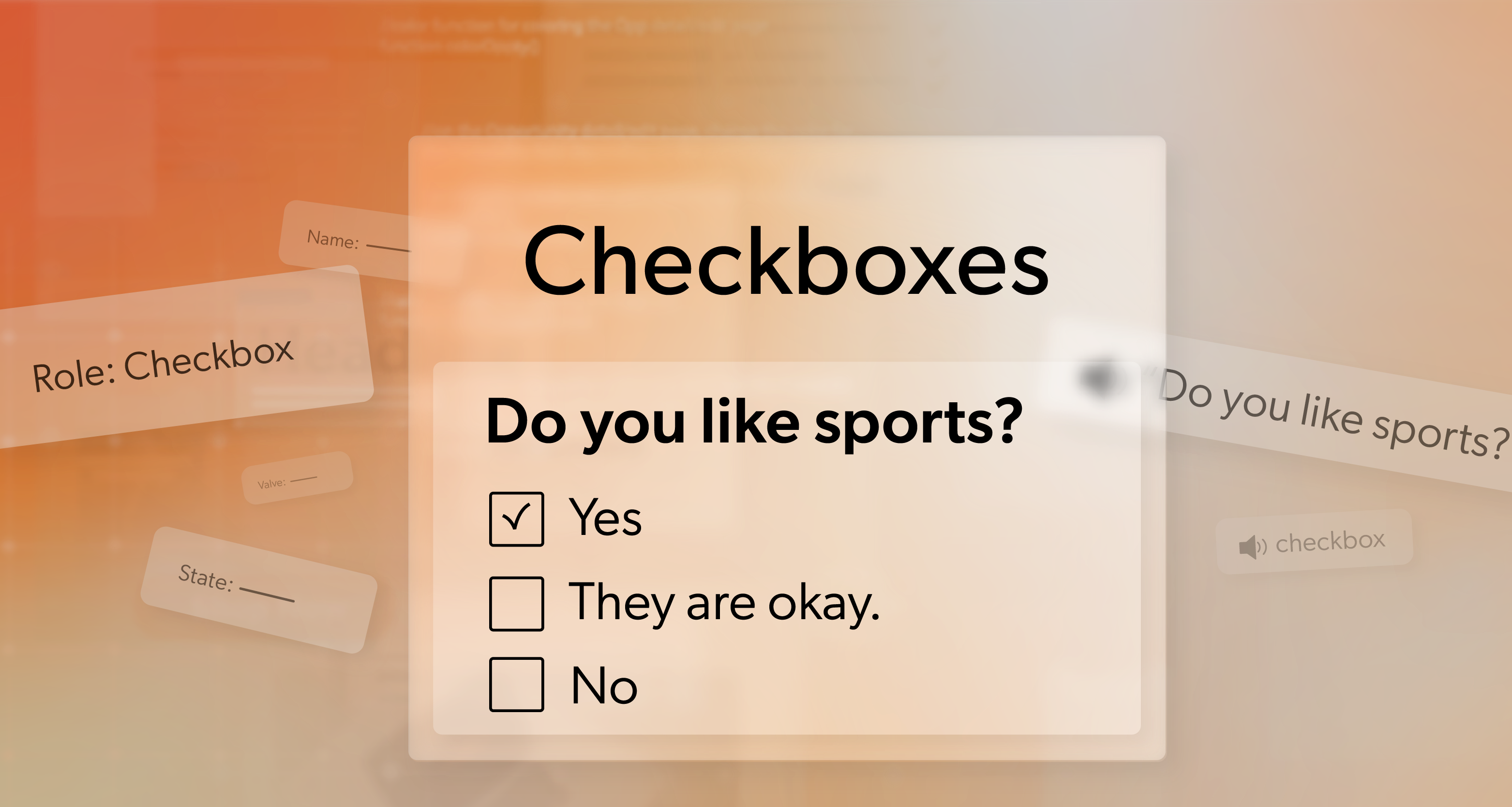
State – What’s Happening Right Now?
The State describes the current condition of an element—checked, selected, expanded, disabled, and more.
Example:
- A checkbox marked checked or unchecked
- A menu marked expanded or collapsed
Why it matters: Users need to know what changed when they interact.
Tip: Update states programmatically when elements change.
Value – What’s Inside?
The Value describes what the element holds or represents.
Examples:
- The number on a range slider
- Text inside an input field
Why it matters: Value tells users the meaningful data inside a component.
Tip: Make sure values are programmatically determinable, not only visual.
WCAG 4.1.2 in Practice: Using Elements Correctly
WCAG 4.1.2 is easier to meet when you let semantic elements do the heavy lifting. Trouble often begins when developers override built-in behavior to create custom widgets.
Avoid Non-Semantic Interactive Elements
Turning <div> and <span> elements into buttons or toggles breaks built-in accessibility. Without the right roles, keyboard support, and states, users get stuck.
Prefer:
<button>for actions<a href>for navigation
Avoid Overreliance on ARIA
ARIA is powerful—but it doesn’t replace semantic HTML.
Before using ARIA, ask:
- Can a native element do this?
Keep States Updated
Custom menus, modals, and sliders often fail when values and states don’t update programmatically.
Native elements like <details>, <input type="range">, <progress>, and <meter> handle these states automatically.
Label and Group Clearly
Label every control. Connect labels using for and id. Group related controls with <fieldset> and <legend>.
Get Focus and Keys “For Free”
Native controls include keyboard behavior and focus management. Custom widgets require rebuilding that logic—and often fall short.
Quick Micro-Checklist
- Can I use native HTML?
- Is there a visible label and accessible Name?
- Does the component handle its own State and Role?
Most fixes are simpler than they seem. The right element often solves the problem.
Building with Clarity: Practical Tips
Creating strong accessibility starts with intentional structure.
- Start with semantics: Use meaningful HTML
- Make states detectable: Keep ARIA states synced via JavaScript
- Label everything: Buttons, fields, toggles
- Test with assistive tech: NVDA, VoiceOver, JAWS
- Remember the human: Every accurate property helps someone navigate with confidence
When these patterns are in place, meeting WCAG 4.1.2 becomes natural.
From Compliance to Connection: Why This Really Matters
Thinking about NSRV is more than rules or checklists. It’s a way to ensure the interface means the same thing to everyone.
Good NSRV means:
- Screen reader users understand visual changes
- Keyboard users can follow focus
- Voice users can activate controls reliably
- Tools—of all kinds—can interact consistently
When Name, State, Role, and Value are aligned, you build experiences that are predictable and smooth. Users gain confidence. The design feels intentional.
And yes, you also meet WCAG 4.1.2, but the value goes far beyond compliance. This is craftsmanship: building software that works everywhere.
WCAG 4.1.2 as a Marker of Quality
Mastering these basics future-proofs your work. Frameworks, libraries, and patterns come and go. But NSRV remains the foundation that browsers, assistive tech, and automation depend on.
Developers who internalize these practices ship interfaces that work—no matter the environment.
It’s more than accessibility. It’s resilience.
Strengthen Your Foundation, Strengthen Your Site
Name, State, Role, and Value form the quiet structure that holds your interface together. Get them right, and your components speak clearly to every device and every user.
If someone can:
- Name the element
- Understand its Role
- Perceive its State
- And hear or see its Value
…they can use it with confidence.
Strong NSRV helps you meet WCAG 4.1.2, but more importantly, it helps you deliver thoughtful, dependable design. When code becomes clear communication, everyone benefits.
If you’re ready to strengthen your website’s foundation, 216digital can help. Our accessibility experts work alongside development teams to audit, teach, and fine-tune interfaces for real-world usability.
Schedule an ADA briefing with 216digital to start building stronger, more accessible experiences from the inside out.