Images are the bread and butter for any website. You put a lot of time and effort into creating engaging visual content for your audiences. But that’s only half of the battle — making your content accessible to as many people as possible is the other half.
Despite the accelerated pace of the digital era, many businesses and organizations still lag behind in making their websites accessible to people with disabilities. This is partly due to the lack of awareness and/or technical knowledge of different web accessibility barriers and how to solve them.
What happens when your users have visual impairments? How do they receive and understand this visual information?
In this article, we answer one of the most commonly asked questions — does my image need alt text to be web accessible?
Image Types And Alternative Text
Before we analyze an image for web accessibility, we must first take a step back and think about its purpose. Is it to inform, evoke emotion, serve as a link, or just for visual appeal?
To understand how to make the image accessible for users with assistive technologies (AT) like screen readers, ask:
- “What is the message the image is trying to convey?”
- “Is the message simple or complex, emotional or actionable?”
An online tool like an image decision tree can help categorize your image. Or, think about if the image disappeared. Would you still understand the content’s meaning without it?
If the answer is yes, the image is purely decorative. However, the image is necessary if the image provides the user with valuable information and context.
Once you determine what kind of image you are working with, there are some basic web accessibility guidelines to consider.
Decorative Images
There is a lot to consider when it comes to decorative images. If you find yourself saying, “But what about X? or “How about Y?” you might need to reevaluate your image as it might not be decorative.
One of the most challenging images to categorize tends to fall in the “emotional” or “mood” category since these images are more subjective. What one person considers decorative, another might consider informative. So, use your best judgment.
Hiding Decorative Images
While decorative images can enhance visual appeal, they don’t convey any meaningful information. If the image is decorative, then programmatically, the image needs to be hidden from assistive technology.
There are several ways to hide alternative text, including using empty or null alt (alt=””), using ARIA role=” presentation”, or implementing the image as a CSS background. This will signal the AT device to ignore this image as it is not vital to understanding the content.
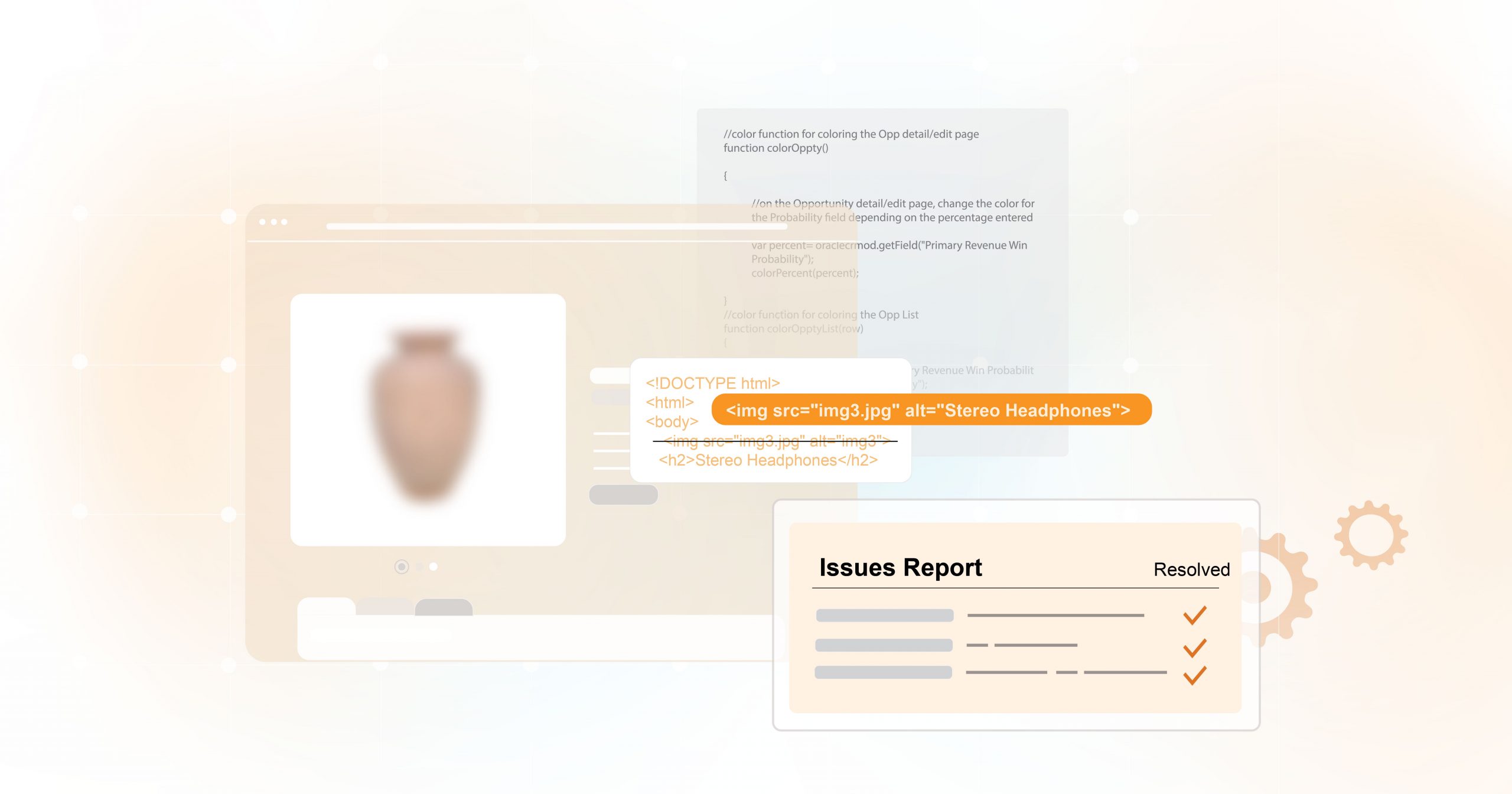
However, it’s important to note that an empty or null alternative text attribute is not the same as a missing attribute. If the alternative text attribute is missing, the AT device might read the file name or surrounding content instead to provide the user with more information about the image.
While aria-hidden= “true” is an option, be cautious, as it will remove the entire element from the accessibility API.
Informative Images
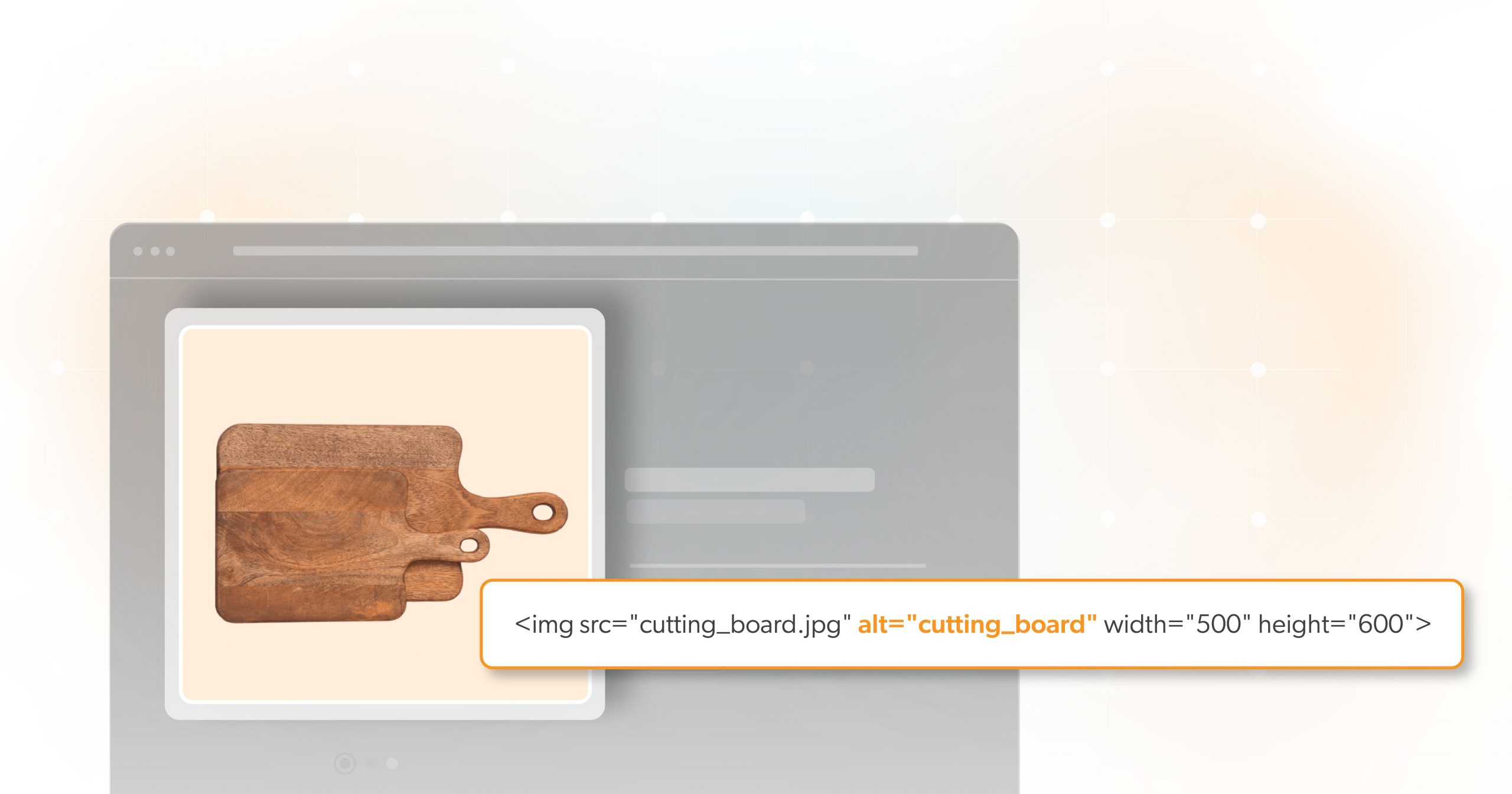
If you decide your image is informative, there are a lot more things to consider. Visually impaired individuals often rely on screen readers to navigate the web. These devices read out textual content, but they can’t “see” images. To bridge this gap, we must have programmatically-discernible alternative text within the website’s HTML.
Alt text is a brief description that conveys the essential information of an image. But having alternate text is not enough — it must also be meaningful. For example, the alt text for a picture of a woman baking might be” Woman baking” — does that convey the whole message? Instead, the alt text should be “Racheal Ray preparing chocolate chip cookies.”
Of course, AT users will have to listen to your alternative text, so do not go overboard. While your descriptions should paint a vivid picture for the user, limiting the number of characters to only 150 is best practice. If you need to add more context to the image, you can use other, more descriptive methods to add more detail.
To learn more about writing alt text, check out our blog post, Understanding Image Alt Text Descriptions.
Charts, Graphs, and Other Complex Images
Sometimes written copy is part of an image, such as in the case of charts, graphs, or diagrams. These images contain too much information to fit into an alt-text description. Instead, you need two parts to describe them. The first part is a short description to identify the image and, if required, the location of the long description. A long description is a textual representation of the essential information conveyed by the image.
Description Containing Structured Information
We can use the <figure> and <figcaption> to associate visible text with an image. When using <figure> and <figcaption>, the alt attribute can be more minimal, and the <figcaption> can be more expressive.
This approach provides a link next to the image that will send the user to a separate web page or a section containing a more detailed description of the image. However, the link text must clarify the destination and associate it with the image. The <figure> and <figcaption> elements can also be used for groups of images.
To identify the complex image, we can also provide accessible names to the image programmatically using the aria-describedby attribute. AT devices will ignore the image’s alt text when these attributes are present and read the ARIA label instead without forcing the users to leave the page. However, this approach can only work if the long description is text-only and does not require structural information.
Meeting Image Accessibility Standards
In an increasingly digital world, ensuring that every user, irrespective of their ability, can access and understand your content is paramount. Ignoring the significant segment of people with disabilities is not only a detriment to your brand’s inclusivity but also a missed opportunity for engagement and growth.
Partnering with 216digital takes the complexity out of the equation, providing expert guidance, tools, and techniques tailored to your needs. We understand that every aspect of your site requires thoughtful consideration, and we’re ready to assist you every step of the way. Don’t leave your web accessibility to chance; schedule a Complimentary ADA Strategy Briefing with our team today, and let us help you make your site truly accessible for everyone.